Business Cycle Phases
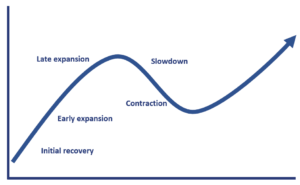
The business cycle can be divided into five distinct phases: (1) initial recovery, (2) early expansion, (3) late expansion, (4) slowdown, and (5) contraction. Business cycle phases are used by economists and fund managers to perform business cycle analysis. Business cycle analysis is used to identify opportunities within the time horizon of a typical business cycle.
On this page, we discuss the main characteristics of each of the business cycle phases.
Initial recovery
The initial recovery is characterized as follows:
- duration of a few months
- business confidence rising
- government stimulus provided by low interest rates and/or budget deficits
- falling inflation
- large output gap
- low or falling short-term interest rates
- bond yields bottoming out
- rising stock prices
- cyclical, riskier assets such as small-cap stocks and high yield bond doing well
Early expansion
The early expansion has the following characteristics:
- duration of a year to several years
- increasing growth with low inflation
- increasing confidence
- rising short-term interest rates
- output gap is narrowing
- stable or rising bond yields
- rising stock prices
Late expansion
The next phase in the business cycle is the late expansion. It is characterised by:
- high confidence and employment
- output gap eliminated and economy at risk of overheating
- increasing inflation
- central bank limits the growth of the money supply
- rising short-term interest rates
- rising bond yields
- rising/peaking stock prices with increased risk and volatility
Slowdown
The slowdown is characterised by:
- duration of a few months to a year or longer
- declining confidence
- inflation still rising
- short-term interest rates at a peak
- bond yields peaking and possibly falling, resulting in rising bond prices
- possible inverting yield curve
- falling stock prices
Contraction
The final business cycle phase is the contraction, which is characterised by:
- duration of 12 to 18 months
- declining confidence and profits
- increase in unemployment and bankruptcies
- inflation topping out
- falling short-term interest rates
- falling bond yields, rising prices
- stock prices increase during the latter stages, anticipating the end of the recession.
Summary
We discussed the main characteristics of the five business cycle phases. This information can be used to determine the current business cycle phase. Alternatively, this information can also be used to position correctly for the next phase of the business cycle.