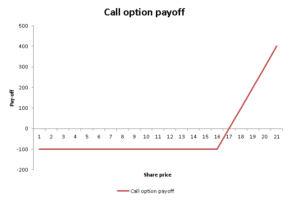
Call option
When investors buy a call option, they are buying the right of buying an underlying during some time in the future at a predefined price today. Note that call option buyers have the right but not the obligation to buy. Hence when the purchase would be unfavourable for them, they can refrain from the purchase. The call option seller on the other hand has the obligation to sell the underlying to the call option buyer. In exchange for this, the seller receives a premium from the buyer.
Call option strategy
Call options are bought in order to anticipate future price increases in the underlying. By purchasing a call option, the buyer is able to get a leveraged exposure to the underlying. Hence, he is able to get a higher return for the same price increase with only a limited investment.
How to buy a call option
A call option can simply be bought on an exchange through your broker. When buying an option, always take into account the option style you are buying, American or European, and the multiple in the underlying. For shares this is usually 100. This means that by buying 1 call, you have the right of buying 100 underlying shares. This is important in order to carefully calculate the exposure to a certain share.
Benefits of a call option
Buying a call option has the benefit of getting a leveraged upside exposure in the market while at the same time limiting downside risk. The maximum loss that can be incurred is the upfront paid option premium. In addition, an increase in volatility, also benefits the option price since it is expected that the underlying is more likely to move in big movements.
Summary
Investors buy call option on a stock or another underlying if they have bullish expectations. This is, when they expect the stock to increase in price over a certain period. By buying a call option, an investor is able to take a leveraged position while at the same time limiting downside risk.
Call option Excel implementation
Need to have more insights? Download our free excel file: call option