Deep Value Investing
Deep value investing is an investment strategy that involves buying stocks or other securities (such as bonds) that are believed to be strongly undervalued by the market. Deep value investors look for companies that are in financial distress. These companies typically have very low price-to-earnings ratios, price-to-book ratios, or other measures of valuation.
Deep value investing is related to traditional value investing but is more aggressive in nature, in that the strategy actively seeks companies that are in financial distress.
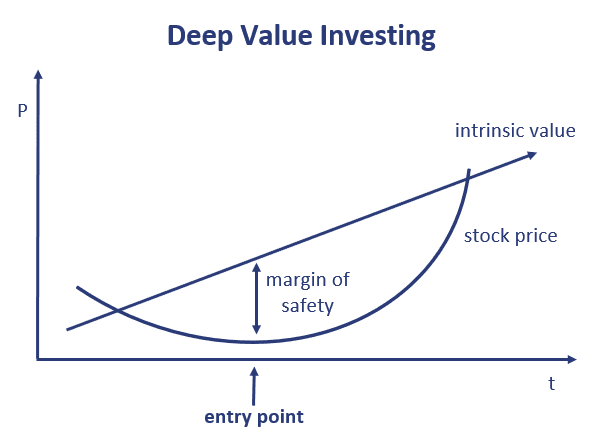
The goal of deep value investing is to find companies that other investors sold off without much regard to longer-term fundamentals. The expectation is that the company will be able to successfully turnaround its business and survive.
Deep value investors will sometimes need to hold their investments for a longer period of time. That is because it may take time for the companies to restructure and make a profit again. Thus, deep value investors should be more patient and willing to wait until the companies’ situation improves.
To implement a deep value investing strategy, an investor will typically do extensive research on a company’s financial health, management, and industry prospects, looking for factors that suggest the company can successfully turnaround. This can involve analyzing financial statements, reading company reports and news articles, and speaking with management or industry experts.
Advantages and disadvantages of Deep Value investing
First, let’s discuss the advantages of deep value investing:
- High returns: By investing in distressed companies, deep value investors can realize substantial gains if the company can survive and become profitable again.
- Diversification: it is a strategy that is very much uncorrelated to the general market. Thus, investors can achieve diversification, reducing their risk and improving the Sharpe ratio of their overall portfolio.
- Contrarian approach: the strategy is a contrarian approach that goes against the crowd, which can provide an edge in the market and result in higher returns. In particular, this kind of investing tries to exploit other investors’ emotional overreaction to bad news.
- Focus on fundamentals: Deep value investors focus on a company’s financial and operational metrics. Fundamental analysis can uncover hidden value not yet identified by the market.
There are also important disadvantages to deep value investing:
- Time horizon: it is a long-term strategy for the patient. Investors should also be willing to hold onto investments even when they continue to suffer in the short term.
- Risk of permanent loss of capital: Some deep value investments will never recover and result in permanent losses. Investors need to prepare for this possibility.
- Lack of liquidity: distressed stocks are not as liquid as other investments. This means that it can be impossible to exit a position in the short run.
- Difficulty in identifying value: It can be challenging to accurately identify undervalued companies, and even when a company appears to be undervalued, there may be good reasons for its low price.
Deep value Investing Example
An example of deep value investing might be buying shares of a company that has a low price-to-earnings ratio and is experiencing temporary financial difficulties. At the same time, the company has valuable underlying assets, such as a valuable brand, a solid customer base, or significant intellectual property.
To make it a bit more concrete, imagine we come across a company that is trading at a price-to-earnings ratio of 3, which is significantly lower than the industry average of 15. Upon further research, the investor discovers that the company is facing some short-term headwinds and is very indebted. Declining revenue due to a temporary economic downturn makes the repayment of the debt uncertain. At the same time, the company has a strong balance sheet, a well-regarded brand, and a loyal customer base.
Our value investor may conclude that the company is undervalued by the market and decide to purchase shares because he expects the company to pull through.
Summary
Overall, deep value investing is a very rewarding strategy for those willing to do their due diligence, have a long-term investment horizon, and have a very high tolerance for risk. At the same time, some investments will fail, leading to a permanent loss of capital for a small part of the portfolio.